 |
SuperNOVAS v1.5
The NOVAS C library, made better
|
 |
SuperNOVAS v1.5
The NOVAS C library, made better
|
Various functions to transform rectangular equatorial vectors (positions or velocities) between different equatorial coordinate systems. More...
Functions | |
| double | app_to_cirs_ra (double jd_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, double ra) |
| Converts an apparent right ascension coordinate (measured from the true equinox of date) to a CIRS R.A., measured from the CIO. | |
| short | cel2ter (double jd_ut1_high, double jd_ut1_low, double ut1_to_tt, enum novas_earth_rotation_measure erot, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, enum novas_equatorial_class coordType, double xp, double yp, const double *in, double *out) |
| double | cirs_to_app_ra (double jd_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, double ra) |
| Converts a CIRS right ascension coordinate (measured from the CIO) to an apparent R.A. | |
| int | cirs_to_gcrs (double jd_tdb, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from the Celestial Intermediate Reference System (CIRS) frame at the given epoch to the ICRS / GCRS. | |
| int | cirs_to_itrs (double jd_tt_high, double jd_tt_low, double ut1_to_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, double xp, double yp, const double *in, double *out) |
| Rotates a position vector from the dynamical CIRS frame of date to the Earth-fixed ITRS frame (IAU 2000 standard method). | |
| int | cirs_to_tod (double jd_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from the Celestial Intermediate Reference System (CIRS) at the given epoch to the True of Date (TOD) reference system. | |
| int | frame_tie (const double *in, enum novas_frametie_direction direction, double *out) |
| Transforms a vector from the dynamical reference system to the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS), or vice versa. | |
| short | gcrs2equ (double jd_tt, enum novas_dynamical_type sys, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, double rag, double decg, double *restrict ra, double *restrict dec) |
| Converts GCRS right ascension and declination to coordinates with respect to the equator of date (mean or true). | |
| int | gcrs_to_cirs (double jd_tdb, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from the ICRS / GCRS to the Celestial Intermediate Reference System (CIRS) frame at the given epoch. | |
| int | gcrs_to_j2000 (const double *in, double *out) |
| Changes ICRS / GCRS coordinates to J2000 coordinates. | |
| int | gcrs_to_mod (double jd_tdb, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from the ICRS / GCRS to the Mean of Date (MOD) reference frame at the given epoch. | |
| int | gcrs_to_tod (double jd_tdb, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from the ICRS / GCRS to the True of Date (TOD) reference frame at the given epoch. | |
| int | itrs_to_cirs (double jd_tt_high, double jd_tt_low, double ut1_to_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, double xp, double yp, const double *in, double *out) |
| Rotates a position vector from the Earth-fixed ITRS frame to the dynamical CIRS frame of date (IAU 2000 standard method). | |
| int | itrs_to_tod (double jd_tt_high, double jd_tt_low, double ut1_to_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, double xp, double yp, const double *in, double *out) |
| Rotates a position vector from the Earth-fixed ITRS frame to the dynamical True of Date (TOD) frame of date (pre IAU 2000 method). | |
| int | j2000_to_gcrs (const double *in, double *out) |
| Change J2000 coordinates to ICRS / GCRS coordinates. | |
| int | j2000_to_tod (double jd_tdb, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from J2000 coordinates to the True of Date (TOD) reference frame at the given epoch. | |
| int | mod_to_gcrs (double jd_tdb, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from Mean of Date (MOD) reference frame at the given epoch to the ICRS / GCRS. | |
| short | ter2cel (double jd_ut1_high, double jd_ut1_low, double ut1_to_tt, enum novas_earth_rotation_measure erot, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, enum novas_equatorial_class coordType, double xp, double yp, const double *in, double *out) |
| int | tod_to_cirs (double jd_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from the True of Date (TOD) reference system to the Celestial Intermediate Reference System (CIRS) at the given epoch to the . | |
| int | tod_to_gcrs (double jd_tdb, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from True of Date (TOD) reference frame at the given epoch to the ICRS / GCRS. | |
| int | tod_to_itrs (double jd_tt_high, double jd_tt_low, double ut1_to_tt, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, double xp, double yp, const double *in, double *out) |
| Rotates a position vector from the dynamical True of Date (TOD) frame of date the Earth-fixed ITRS frame (pre IAU 2000 method). | |
| int | tod_to_j2000 (double jd_tdb, enum novas_accuracy accuracy, const double *in, double *out) |
| Transforms a rectangular equatorial (x, y, z) vector from True of Date (TOD) reference frame at the given epoch to the J2000 coordinates. | |
Various functions to transform rectangular equatorial vectors (positions or velocities) between different equatorial coordinate systems.
The implementations follow the latest standard for high-precision astrometry as described the IAU 2000 / IAU 2006 and IERS 2010 conventions. See Figure 1 below for an overview of the various coordinate reference systems, and the functions, which can be used to tansform position and/or velocoty vectors among them,
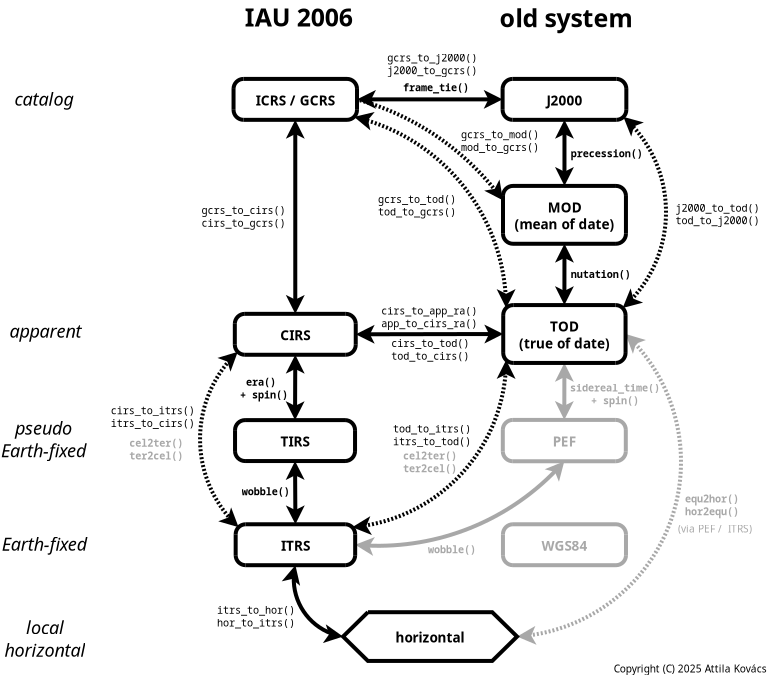
The same transformations are also available for the new frame-based approach via a novas_transform, often with significantly higher computational efficiency.
For the conversion between GCRS and CIRS, the IERS Conventions 2010, Chapter 5 (Section 5.9) describes two equivalent methods:
The two methods are equivalent both in terms of accuracy, down to the μas level, and in terms of computational cost. Neither is 'superior' to the other in any measurable way. In SuperNOVAS we choose to follow Method 2, since its implementation is more readily given with the existing framework of related functions.
REFERENCES:
| short cel2ter | ( | double | jd_ut1_high, |
| double | jd_ut1_low, | ||
| double | ut1_to_tt, | ||
| enum novas_earth_rotation_measure | erot, | ||
| enum novas_accuracy | accuracy, | ||
| enum novas_equatorial_class | coordType, | ||
| double | xp, | ||
| double | yp, | ||
| const double * | in, | ||
| double * | out ) |
Rotates a vector from the celestial to the terrestrial system. Specifically, it transforms a vector in the GCRS, or the dynamical (CIRS or TOD) frames to the ITRS (a rotating Earth-fixed system) by applying rotations for the GCRS-to-dynamical frame tie, precession, nutation, Earth rotation, and polar motion.
If 'system' is NOVAS_CIRS then method EROT_ERA must be used. Similarly, if 'system' is NOVAS_TOD then method must be EROT_ERA. Otherwise an error 3 is returned.
If both 'xp' and 'yp' are set to 0 no polar motion is included in the transformation.
REFERENCES:
| jd_ut1_high | [day] High-order part of UT1 Julian date. | |
| jd_ut1_low | [day] Low-order part of UT1 Julian date. | |
| ut1_to_tt | [s] TT - UT1 Time difference in seconds | |
| erot | Unused. | |
| accuracy | NOVAS_FULL_ACCURACY (0) or NOVAS_REDUCED_ACCURACY (1) | |
| coordType | Input coordinate class, NOVAS_REFERENCE_CLASS (0) or NOVAS_DYNAMICAL_CLASS (1). Use the former if the input coordinates are in the GCRS, and the latter if they are CIRS or TOD (the 'erot' parameter selects which dynamical system the input is specified in.) | |
| xp | [arcsec] Conventionally-defined X coordinate of celestial intermediate pole with respect to ITRS pole. If you have defined pole offsets the old (pre IAU2000) way, via cel_pole(), then use 0 here. | |
| yp | [arcsec] Conventionally-defined Y coordinate of celestial intermediate pole with respect to ITRS pole. If you have defined pole offsets the old (pre IAU2000) way, via cel_pole(), then use 0 here. | |
| in | Input position vector, geocentric equatorial rectangular coordinates in the specified input coordinate system (GCRS if 'class' is NOVAS_REFERENCE_CLASS; or else either CIRS if 'erot' is EROT_ERA, or TOD if 'erot' is EROT_GST). | |
| [out] | out | ITRS position vector, geocentric equatorial rectangular coordinates (terrestrial system). It can be the same vector as the input. |
References era(), EROT_ERA, EROT_GST, gcrs_to_cirs(), gcrs_to_tod(), NOVAS_DYNAMICAL_CLASS, NOVAS_FULL_ACCURACY, novas_gast(), NOVAS_REDUCED_ACCURACY, spin(), wobble(), WOBBLE_PEF_TO_ITRS, and WOBBLE_TIRS_TO_ITRS.
| short ter2cel | ( | double | jd_ut1_high, |
| double | jd_ut1_low, | ||
| double | ut1_to_tt, | ||
| enum novas_earth_rotation_measure | erot, | ||
| enum novas_accuracy | accuracy, | ||
| enum novas_equatorial_class | coordType, | ||
| double | xp, | ||
| double | yp, | ||
| const double * | in, | ||
| double * | out ) |
Rotates a vector from the terrestrial to the celestial system. Specifically, it transforms a vector in the ITRS (rotating earth-fixed system) to the True of Date (TOD), CIRS, or GCRS (a local space-fixed system) by applying rotations for polar motion, Earth rotation (for TOD); and nutation, precession, and the dynamical-to-GCRS frame tie (for GCRS).
If 'system' is NOVAS_CIRS then method EROT_ERA must be used. Similarly, if 'system' is NOVAS_TOD then method must be EROT_ERA. Otherwise an error 3 is returned.
If both 'xp' and 'yp' are set to 0 no polar motion is included in the transformation.
REFERENCES:
| jd_ut1_high | [day] High-order part of UT1 Julian date. | |
| jd_ut1_low | [day] Low-order part of UT1 Julian date. | |
| ut1_to_tt | [s] TT - UT1 Time difference in seconds | |
| erot | Unused. | |
| accuracy | NOVAS_FULL_ACCURACY (0) or NOVAS_REDUCED_ACCURACY (1) | |
| coordType | Output coordinate class NOVAS_REFERENCE_CLASS (0, or any value other than 1) or NOVAS_DYNAMICAL_CLASS (1). Use the former if the output coordinates are to be in the GCRS, and the latter if they are to be in CIRS or TOD (the 'erot' parameter selects which dynamical system to use for the output.) | |
| xp | [arcsec] Conventionally-defined X coordinate of celestial intermediate pole with respect to ITRS pole. If you have defined pole offsets the old (pre IAU2000) way, via cel_pole(), then use 0 here. | |
| yp | [arcsec] Conventionally-defined Y coordinate of celestial intermediate pole with respect to ITRS pole. If you have defined pole offsets the old (pre IAU2000) way, via cel_pole(), then use 0 here. | |
| in | Position vector, geocentric equatorial rectangular coordinates, referred to ITRS axes (terrestrial system) in the normal case where 'option' is NOVAS_GCRS (0). | |
| [out] | out | Position vector, equatorial rectangular coordinates in the specified output system (GCRS if 'class' is NOVAS_REFERENCE_CLASS; or else either CIRS if 'erot' is EROT_ERA, or TOD if 'erot' is EROT_GST). It may be the same vector as the input. |
References cirs_to_gcrs(), era(), EROT_ERA, EROT_GST, NOVAS_DYNAMICAL_CLASS, NOVAS_FULL_ACCURACY, novas_gast(), NOVAS_REDUCED_ACCURACY, spin(), tod_to_gcrs(), wobble(), WOBBLE_ITRS_TO_PEF, and WOBBLE_ITRS_TO_TIRS.